Hyperspectral imaging captures detailed material information across hundreds of spectral bands; however, its real-world use has been limited by the scarcity of labeled data and sensor differences. In a study published in IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, Professor ZHANG Geng and his teamfrom Xi'an Institute of Optics and Precision Mechanics (XIOPM) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences developed the SpectralDINO, an innovative framework that effectively bridges visual foundation models with hyperspectral data, enabling more efficient and adaptable remote sensing analysis.
SpectralDINO combines several advanced strategies to tackle cross-domain challenges. It first aligns spectral information from source domains to establish a consistent feature space. The framework also incorporates a dual-subspace hybrid low-rank adaptation (LoRA) module, empowered by cross-domain attention, to accurately identify and separate features from different sensors. Together, these techniques allow the model to learn robustly from very few labeled examples.
In experiments on three public datasets, Pavia University, Salinas, and Houston, SpectralDINO achieved overall accuracies of 88.15%, 92.02%, and 81.67%, outperforming existing methods by about 4%. Notably, it reached this performance by tuning only 1.14% of the model parameters, greatly lowering computational costs. Visualization studies further confirmed the model’s ability to extract meaningful and transferable spectral features
“SpectralDINO enables efficient transfer of visual foundation models to hyperspectral learning with minimal samples, demonstrating strong generalization. It offers practical value for remote sensing and agriculture, with future work extending to multimodal and temporal analysis,” said Prof. ZHANG Geng from XIOPM.
(Published 3 October 2025)
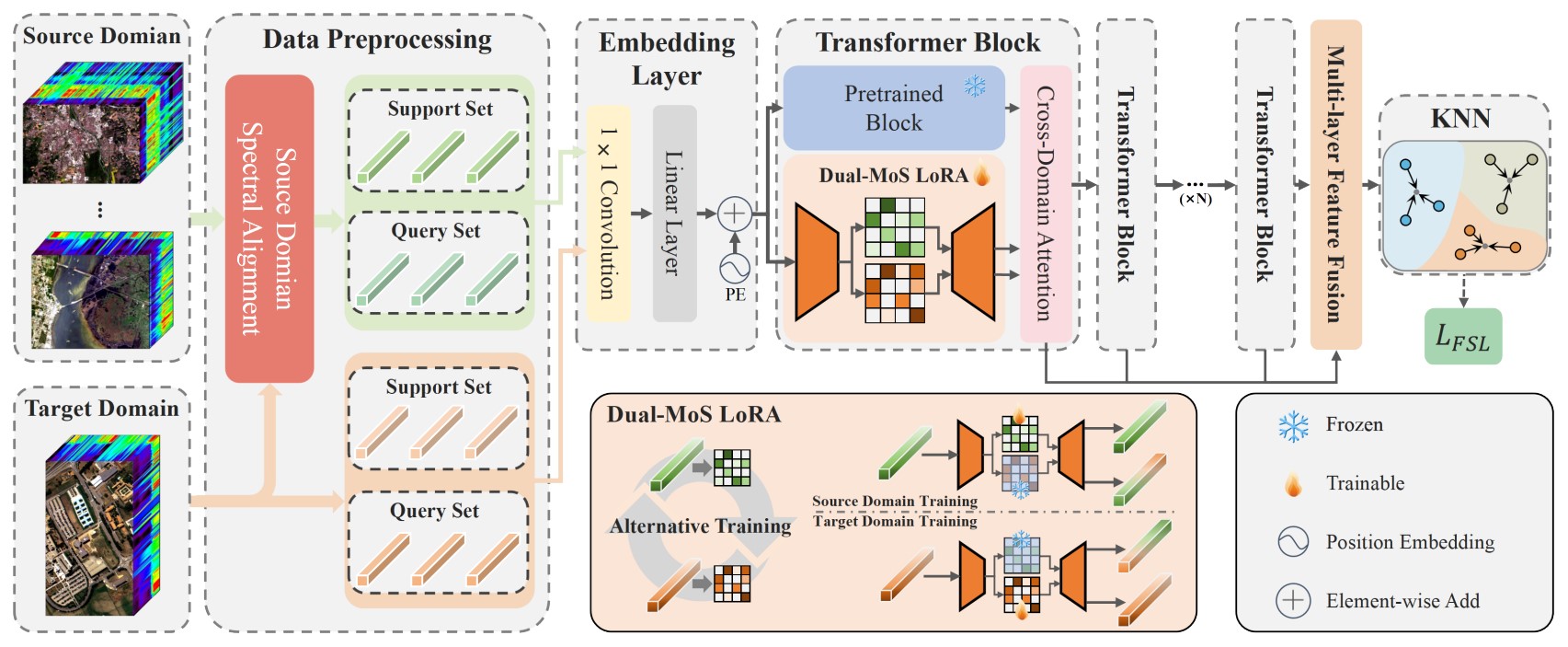
Figure. Schematic of the SpectralDINO framework. (Image by XIOPM)
Download: