Recently, a research group led by Prof. LI Haiwei from Xi’an Institute of Optics and Precision Mechanics (XIOPM) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences proposed an innovative approach called the adaptive generalization-driven methodology, which aims to obtain high-precision Bidirectional Reflectance Distribution Function (BRDF) modeling using Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV)-borne multispectral remote sensing. This achievement enables centimeter-to-kilometer scale reflectance characterization across diverse landscapes.
The research results were published in ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing.
BRDF is extremely critical for quantifying anisotropic reflectance properties of land surfaces, with applications in satellite calibration, vegetation monitoring, and aerosol inversion. However, traditional satellite-based BRDF products often lack the spatial resolution and timeliness required for precise large-area modeling. Fortunately, UAV technology offers a solution by enabling efficient multi-angle data acquisition at high resolution.
The research team employed a DJI M600 drone equipped with a Red-Edge multispectral imager to implement a multi-rectangle nested flight scheme. This approach captured pixel-level multi-angle data across five spectral bands (475 nm, 560 nm, 668 nm, 717 nm, and 840 nm) for six feature types: grass, water, bare ground, trees, concrete roads, and standard targets. To ensure data accuracy, illumination variations were monitored in real-time using an irradiance measurement device, while slope and aspect were derived from reconstructed maps.
Based on the comprehensive dataset, the team established a standardized multi-angle information database integrating imagery, terrain, and lighting conditions, which are expected to create a robust foundation for precise modeling. Therefore, the three widely used surface reflectance models could be enhanced to better accommodate complex variables like illumination dynamics and terrain undulations.
Experimental results showed that the corrected BRDF models reduced fitting errors significantly, with root mean square errors (RMSE) as low as 0.0109. The adaptive diffusion method identified optimal observation areas for each feature, such as a 2111.71 m2 region for grass and a 351.99 m2 area for water.
"The integration of UAV data with adaptive BRDF modeling opens new possibilities for high-resolution, large-scale remote sensing applications. And this method not only improves classification accuracy but also enhances the efficiency of reflectance inversion in complex environments,” said Prof. LI Haiwei.
(Available online 4 June 2025)
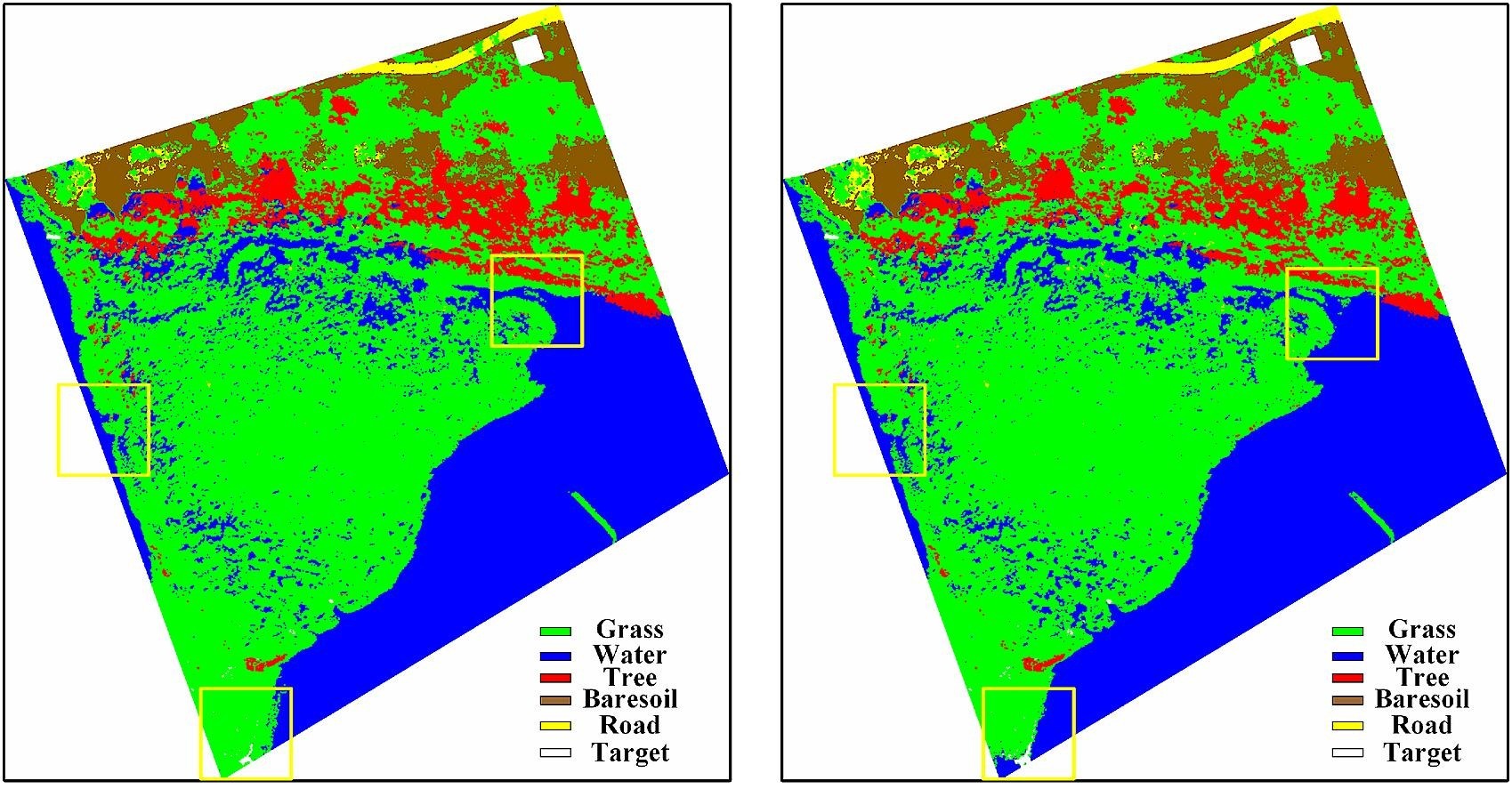
Fig. The SVM pre-classification results and Enhanced SVM Classification Results with Highly Accurate BRDF Models. (Image by XIOPM)
Download: