In various space tasks such as space rendezvous-docking and on-orbit maintenance, the measurement of the relative posture and position of non-cooperative spacecraft is a key premise. However, the commonly used global positioning system, radar detection systems and laser scanners are not suitable for certain special space tasks as they are large, heavy, complex and expensive.
The computer vision has good performance recently in many important space missions due to its low cost, small size, light mass and acceptable accuracy. But for space missions require high accuracy or using wide-angle lenses especially the lens needs to withstand harsh mechanical and thermal conditions in space for a long time, the traditional pinhole model is not sufficient.
A research team led by Prof. ZHANG Gaopeng from Xi’an Institute of Optics and Precision Mechanics (XIOPM) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) reported an on-orbit distortion parameter calibration method based on vanishing point consistency. The study was published in Optics and Lasers in Engineering.
As solar panels are commonly utilized in most spacecraft, the space environment cannot use specific calibration objects, and the available geometric information is limited, solar panels were used to achieve on-orbit distortion parameter calibration.
The method proposed in this study mainly includes the accurate estimation of the vanishing point position, establishment of the objective function according to the vanishing point consistency constraint and the optimization and solution of the distortion parameters through the improved genetic algorithm (IGA). Then, the on-orbit solution of the distortion parameters for the space camera was completed. Quantitative analysis was performed through simulation experiments to obtain the effects of different influencing factors.
The distortion calibration method provides better performance than Brown’s method in terms of accuracy. In physical experiment, clear correction traces can be seen from the base of the satellite model. The experiment indicated that this method can realize the distortion correction of the space target image. It is flexible and robust for various space tasks like rendezvous and docking.
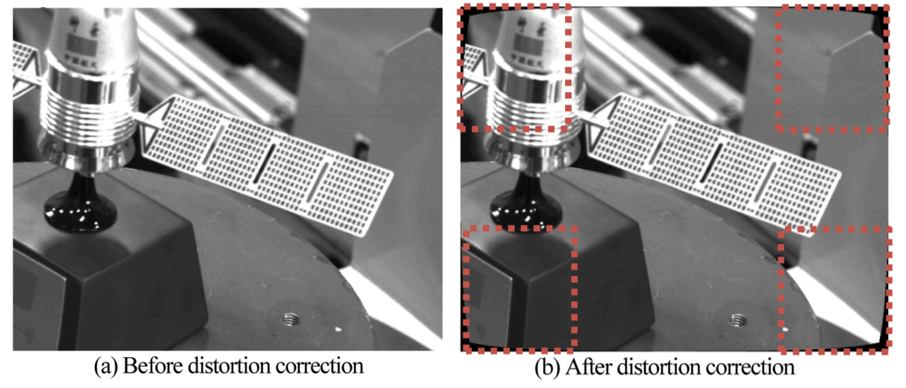
Fig. Before versus after distortion correction((Image by ZHANG et al.)
Download: