Reflective optical system as a key element in space remote sensing, which is widely employed in space to earth communication, has attracted great interests recently. However, the current systems cannot simultaneously satisfy the requirement of high image quality and small relative aperture.
It is known that the large relative aperture will introduce aberrations that eventually lower the quality of images. Therefore, the balance between field of view and relative aperture is extremely important for improving the optical systems.
Are there any methods to address the difficulties and prompt the development of image-side telecentric systems?
A research team led by Dr. LI Xijie from Xi'an Institute of Optics and Precision Mechanics (XIOPM) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) proposed a novel design to solve the mentioned issues by using coaxial parent mirrors. The results were published in OPTIK.
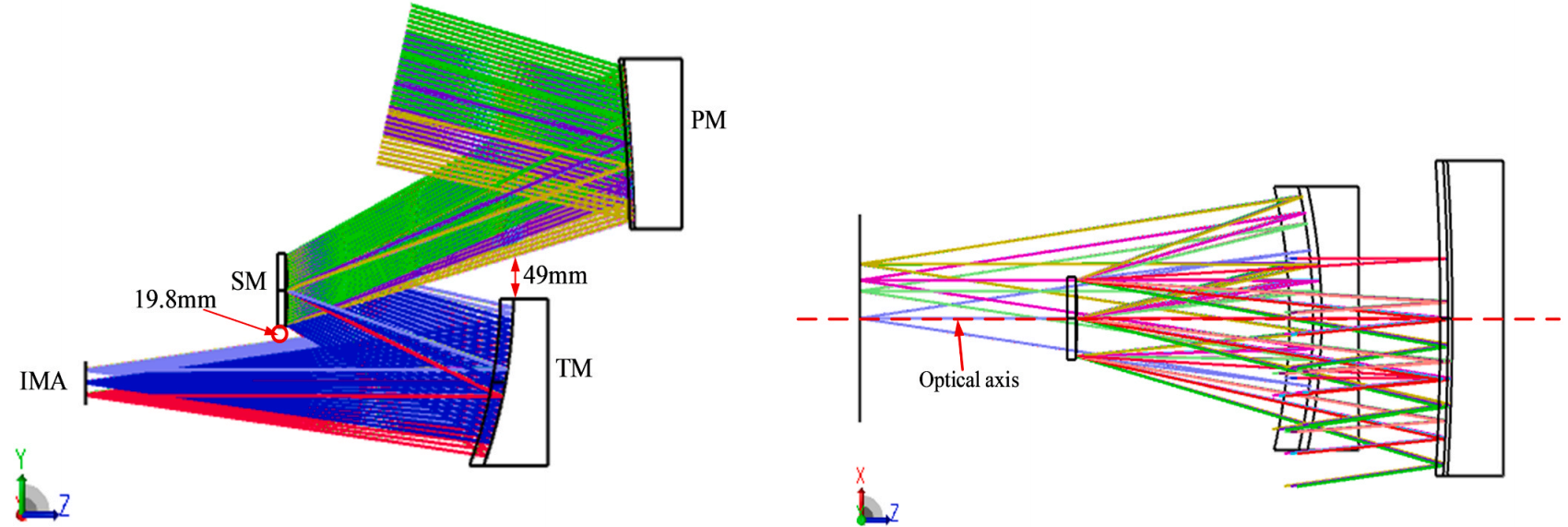
Off-axis system based on the coaxial parent mirrors. (Image by XIOPM)
“We use the optical path difference formula to established the initial configuration and complete the entire system by further optimizing the functions of field bias, aberration, and tolerance sensitivity.” said Dr. LI.
Through the delicately design, the results indicate that the system with a focus of 400 mm, a relative aperture of 1/3, and an FOV of 18? × 6? is finally obtained. Moreover, the modulation transfer function is greater than 0.7 at 34 IP/mm.
The maximum offset of the spectral smile, which can influence the performance of the imaging system, is 0.37 mm and 0.91 mm in the meridional and sagittal directions implying the imaging quality is close to the diffraction limitation
This study can pave the way for the development of image-side telecentric systems with remarkable performance.
Contact:
SHE Jiangbo
Xi'an Institute of Optics and Precision Mechanics
E-mail: shejb@opt.ac.cn
Date of Publication: 2021-04-20
Download: