Visual tracking has drawn constant attention of the researchers and engineers over the last decades. Some novel applications are also inspired by the improvement of related research, such as auto-track by drone, pose recognition by mobile payment, and remote control by space robot.
Although the researchers are making much progress persistently, it is still a vital problem to achieve a tracking procedure that simultaneously balances the accuracy, robustness, and tracking speed under complex scenarios, such as occlusion, illumination change, and scale variation.
Much progress has made by the combined region proposal networks (RPN) and Siamese networks recently. There are still some vital problems have not been settled during tracking procedure, such as easy negatives due to sampling process, too many semantic features caused by deep neural networks, which may make the visual tracker inaccurate in spatial location and less robust.
A research team led by Dr. Ximing Zhang from Faculty of Space, Xi'an Institute of Optics and Precision Mechanics (XIOPM) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) proposed a novel tracking strategy to make the camera more intelligent benefitting from accurate and robust visual tracking algorithms.
By analyzing the feature transfer function of the spatial transformer networks, the tracker can solve the spatial transformation problems when suffering from heavy scale change and rotation. Benefiting from the shrinkage loss, the networks penalize the weights of easy samples to alleviate the data imbalance issue. Considering the redundancy of the proposals, we find that multi-cue such as shape, color, and scale can be applied to refine the high-quality proposals that can not only improve the tracking performance in complex scenarios, but also reduce the computational effort. The results were published in SENSORS.
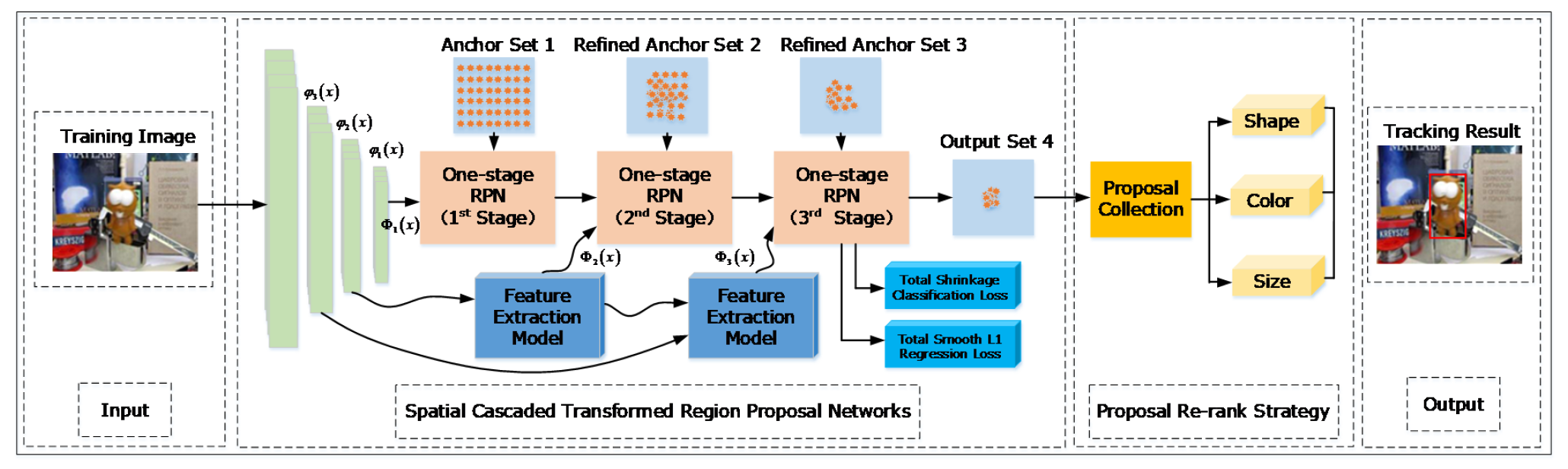 Fig. 1 The workflow of the proposed method and the network architecture (Image by XIOPM)
Fig. 1 The workflow of the proposed method and the network architecture (Image by XIOPM)
By utilizing the proposed method, the paper performs the experimental comparison with state-of-the-art methods in Large-scale Single Object Test Bench, Wild applications and UAV tracking scenarios. The tracker can not only handle accurate tracking in stable platform, but also the robust tracking in fast motion. The related results are performed in Fig. 2.
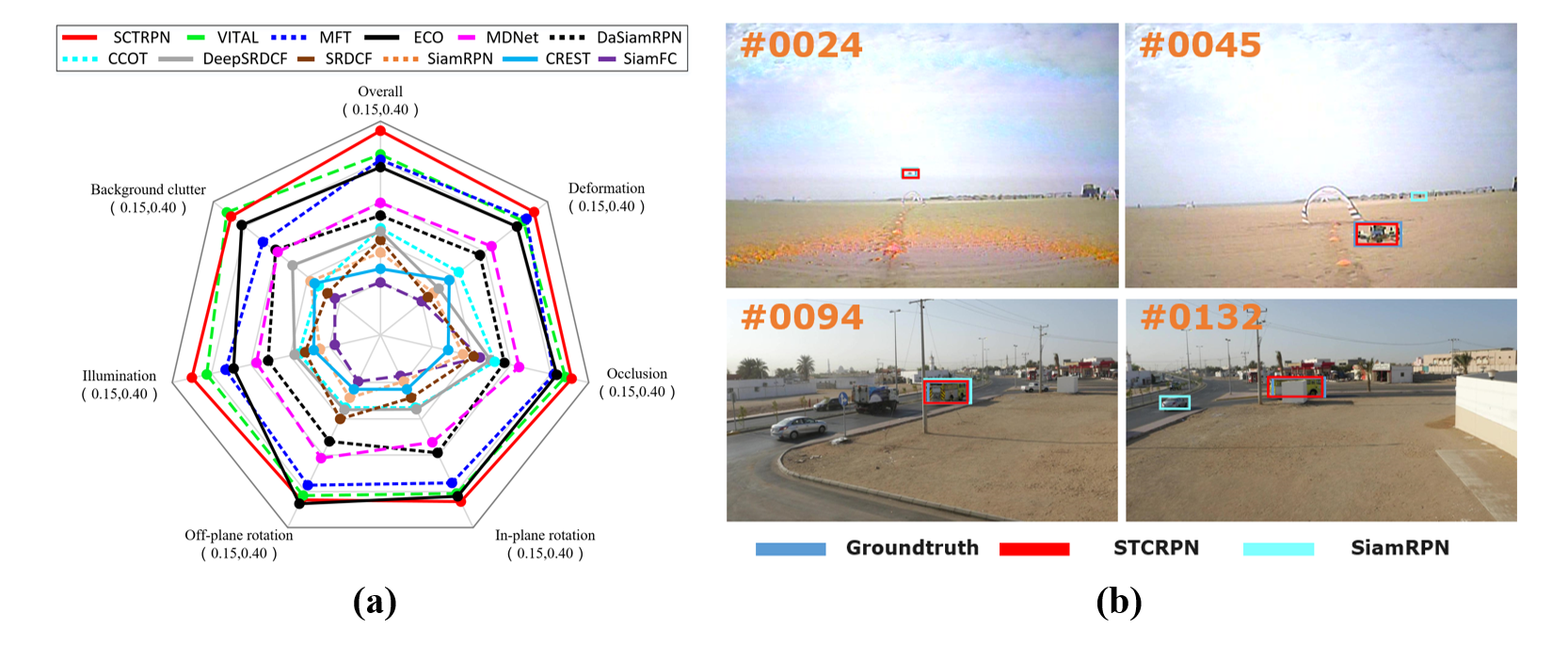 Fig. 2. The related results between the proposed algorithm with state-of-the-art methods (Image by XIOPM)
Fig. 2. The related results between the proposed algorithm with state-of-the-art methods (Image by XIOPM)
The paper provides the novel idea to make the cameras more intelligent through visual tracking algorithm and deep neural networks. In the near future, the scientist will solve the problems of “tracking-by-understanding”, the smart camera would truly think like peoples do.
Download: