Due to the fact that weak and fake laser-induced damages may occur in the surface of optical elements in high-energy laser facilities, it is still a challenging issue to effectively detect the real laser-induced damage changes of optical elements in optical images.
Different from the traditional methods, in this paper, a research team led by Prof. Dr. DA Zhengshang from Xi'an Institute of Optics and Precision Mechanics (XIOPM) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) put forward a similarity metric optimization driven supervised learning model to perform the laser-induced damage change detection task.
In the proposed model, an end-to-end siamese convolutional neural network is designed and trained which can integrate the difference image generating and difference image analysis into a whole network.
Thus, the damage changes can be highlighted by the pre-trained siamese network that classifies the central pixel between input multi-temporal image patches into changed and unchanged classes.
To address the problem of unbalanced distribution between positive and negative samples, a modified average frequency balancing based weighted softmax loss is used to train the proposed network.
Experiments conducted on two real datasets demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of the proposed model.
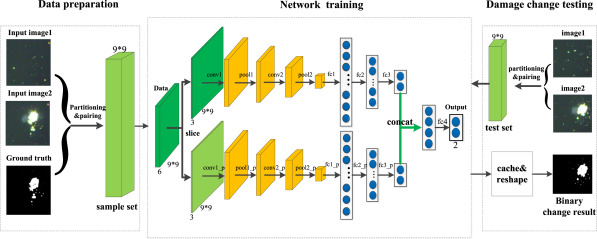
Schematic diagram of the proposed SMO-SCNN model. (Image by XIOPM)
(Original research article "APPLIED SOFT COMPUTING (2020) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2019.106015")
Download: