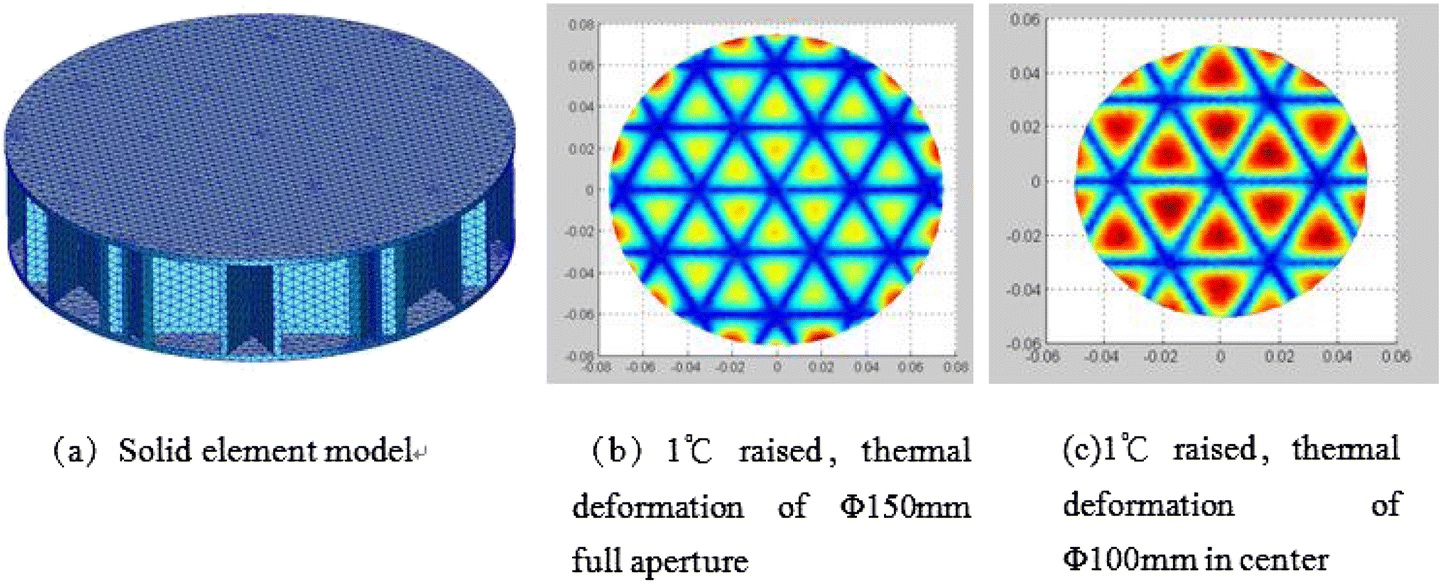
Due to low density, high specific stiffness, and low thermal expansion, carbon fiber reinforced plastic (CFRP) is one of potential materials for high precise components. For high precise structures such as reflectors and optical mirrors, usually strict thermal stability required. In order to ensure rigidity and thermal deformation resistance, carbon fiber mirrors are usually designed as a grid-reinforced sandwich structure. In order to improve the thermal stability of carbon fiber mirrors, Liang Xu’s research team propose a new type of grid-reinforced sandwich structure design. Finite element method was used to analyze the thermal deformations of the carbon fiber mirror without manufacturing error and with manufacturing error. In order to overcome the effect of moisture absorption deformation, thermal deformation test of the carbon fiber mirror was performed in a vacuum tank. The test results verify the reliability of the finite element analysis results. For phi 100mm center aperture of the phi 150mm carbon fiber mirror, the test results show that the thermal stability is about 4nm/degrees C, which is enough for optical mirror application, although grid effect existed.
(Original research article "Applied Composite Materials Vol. 26, Issue 2, pp. 469-478 (2019) https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs10443-018-9705-1 ")
Download: