Recently, a team led by Prof. LU Xiaoqiang from Xi'an Institute of Optics and Precision Mechanics (XIOPM) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) proposed a novel method for spectral super-resolution of multispectral images using spatial–spectral residual attention network. Their up-to-date result was published on IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON GEOSCIENCE AND REMOTE SENSING.
The purpose of the spectral super-resolution of multispectral image (MSI) is improving the spectral resolution of the MSI to obtain the hyperspectral image (HSI).
Though many remarkable methods have been achieved, researchers observe that the spatial information of MSI cannot be fully explored. The reason is that most recent methods are based on the sparse representation to unfold the MSI into the 2-D matrix in advance for subsequent operations.
To address the above problems, LU and his team members proposed a spatial–spectral residual attention network (SSRAN) to simultaneously explore the spatial and spectral information of MSI for reconstructing the HSI. The whole structure was disassembled into three modules, feature extraction, nonlinear mapping, and reconstruction.
According to the experiments results, the proposed method is superior to the state-of-the-art methods on both simulated and real databases. In the future, the proposed method will provide a guide for designing novel framework of spectral super-resolution of multispectral images.
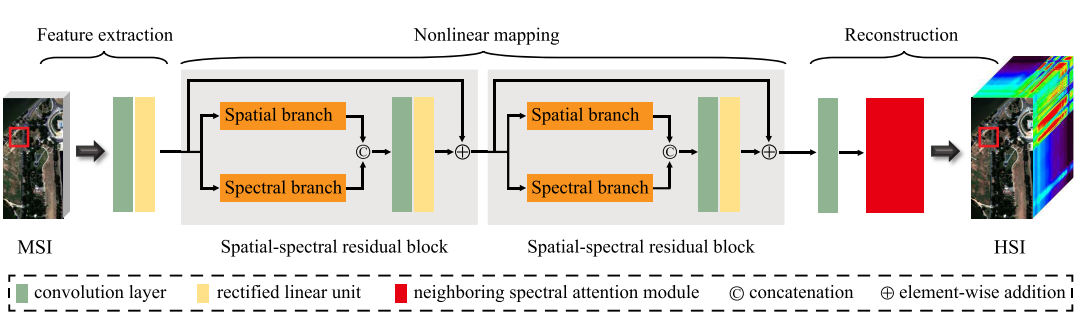 Detailed structures of the proposed SSRAN. (Image by XIOPM)
Detailed structures of the proposed SSRAN. (Image by XIOPM)


