Recently, a team led by Prof. Cao Jianzhong from Xi'an Institute of Optics and Precision Mechanics (XIOPM) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) proposed an image fusion network based on variational auto-encoder (VAE). Their up-to-date result was published on Infrared Physics and Technology.
Infrared and visible image fusion mainly aims at combining infrared radiant features with visible textural features into one image, which contains diverse meaningful information for subsequent processing tasks.
Some recent methods are based on auto-encoder (AE), which has the ability of restoring the original image. However, the researchers observe that if some random changes happen to the feature vectors, the reconstructed image will be obscure or even meaningless. The reason is that some feature vector values have greatly changed from their initial values. It means that AE is not very suitable for this task. Different from AE, VAE can reconstruct images which has similar radiation and detail features to the original image.
Based on the abovementioned observation and analysis, CAO and his team members proposed a new fusion network, which is first utilized VAE in infrared and visible image fusion field and able to meet the requirement for generating a new image from two source images. The whole framework was disassembled into image fusion network and infrared feature compensation network.
According to the experiments results, the proposed method outperforms other traditional and deep learning methods under different evaluation metrics. In the future, the proposed method will provide a guide for designing novel framework for infrared and visible image fusion.
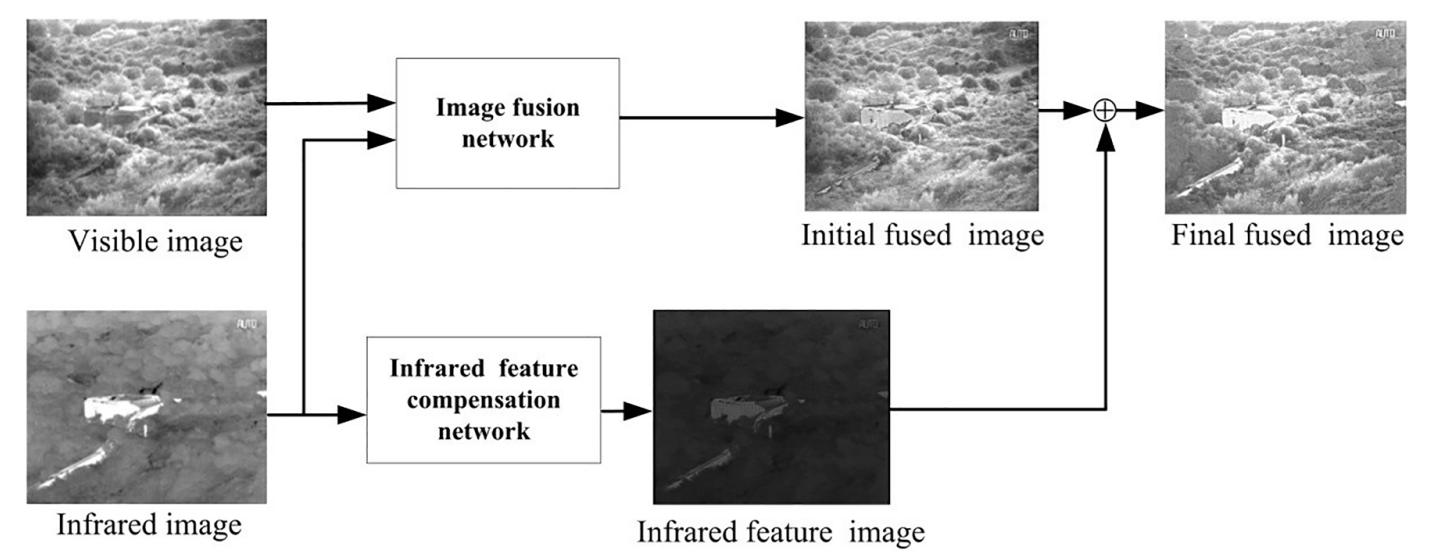 Structure diagram of infrared and visible image fusion network. (Image by XIOPM)
Structure diagram of infrared and visible image fusion network. (Image by XIOPM)


