Recently, a team led by Prof. LU Xiaoqiang from Xi'an Institute of Optics and Precision Mechanics (XIOPM) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) proposed cross-resolution difference learning for unsupervised change detection. Their up-to-date result was published on IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON GEOSCIENCE AND REMOTE SENSING.
Change detection (CD) mainly aims at recognizing the differences between multitemporal images captured over the same geographical area at different times. Compare to methods based on cumbersome labeled change information, unsupervised CD methods can generate a change map without prior knowledge about the change information which has attracted widespread attention.
Moreover, it is difficult to directly detect changes in the practical application, because many multitemporal images captured at different times have different resolutions with different sensor properties. For most existing methods, they usually resized multitemporal images to a unified size which has a negative impact on the final CD performance because of changing the original information of pixels.
To address the above problems, LU and his team members proposed a cross-resolution difference learning method without resizing operations and cumbersome labels. The whole framework was disassembled into three modules, image segmentation, difference learning, and cross-resolution fusion.
According to the experiments results, the effectiveness of the proposed method are demonstrated under different evaluation metrics. In the future, the proposed CD method will provide a guide for designing novel framework of cross-resolution unsupervised change detection.
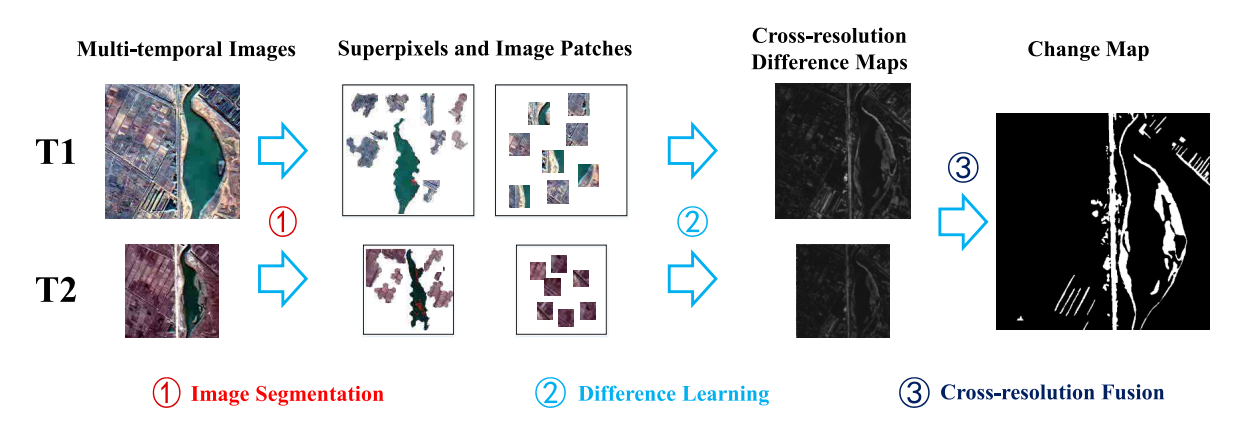
Figure 1. Flowchart of the proposed CD method. (Image by XIOPM)


