Zoom imaging is of great importance in optical system to realize imaging to objects on different distances. Despite the traditional zoom method, zoom imaging without moving elements is attracting more and more attention. The variable curvature mirror (VCM) is the key element which can help to achieve zoom imaging without moving elements through applying external force on it, such as the air pressure, piezoelectric actuators, etc. This type of zooming method is attractive as it can greatly reduce the volume and weight of the optical system compare to traditional zoom system.
A team led by Prof. ZHAO Hui from the Xi’an Institute of Optics and Precision Mechanics (XIOPM) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) had reported that they've done studies on VCM that can realize changing of the curvature radius of the reflective mirror with high surface figure accuracy maintenance simultaneously.
Recently, the same team announced that they designed and manufactured a new variable curvature mirror (VCM) using the material of ultralumin, which shows good performance when actuated by air pressure. Their up-to-date result was published on Journal Optics Express.
In their previous study, they studied and solved the analytical solution of the VCM with a thickness distribution of exponential shape using small parameters method. Through comparing to the finite element analysis result of the same structure parameters, the two have good consistency.
Based on this, they worked out the analytical solution of thin elastic plate with a cycloid-like thickness distribution also by the same approximate method. Furthermore, a VCM with a cycloid like thickness distribution is also designed, manufactured, processed and experimented. With an original surface figure accuracy about λ/80, the VCM can achieve about 37μm central deflection under pressure value of 0.07MPa. the surface figure accuracy after actuated is about λ/10, λ/40 which is with and without spherical aberration separately.
The air pressure actuated VCM shows advantages over VCMs actuated by other methods, such as the uniform force distribution, better contact. It can realize a good surface shape which could not be easy to achieve by mechanical movement due to the contact problem between the mechanical structures.
The good surface performance of the VCM will have the potential to be applied in imaging systems in the visible light band, for example, the space imaging camera, earth-based telescope.
Moreover, on the base of systematical theoretical and experimental analysis, the team figured out what it could be when a VCM with cycloid-like thickness distribution is actuated by uniform pressure, the main aberration it has after actuation, also the analytical solution of the elastic plate with this shape.
These new results provide guides for further improving the structure design and optimization in the future.
This work was supported by the West Light Foundation of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Research Fund for Young Star of Science and Technology in Shaanxi Province, China Scholarship Council.
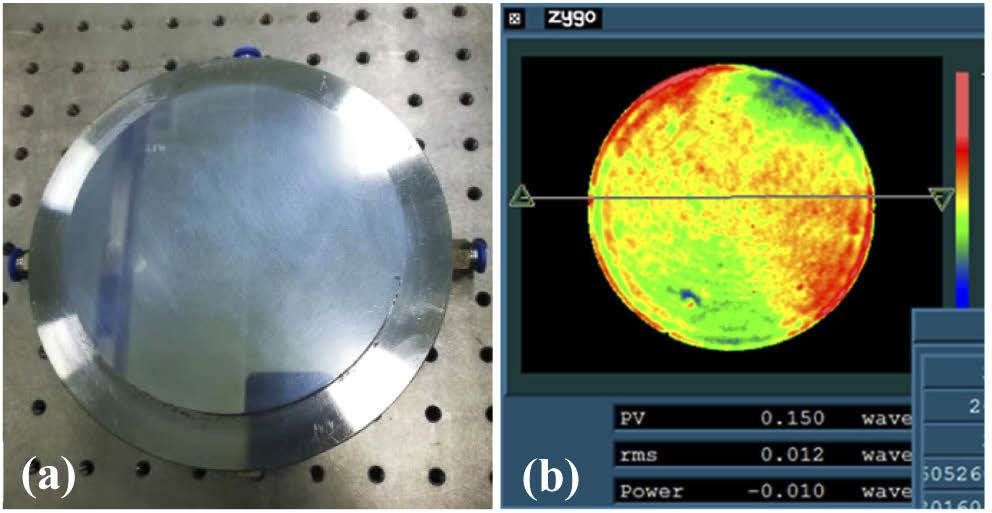 (a) And (b) represent the VCM and its original surface figure accuracy after ion beam figuring. (Image by XIOPM)
(a) And (b) represent the VCM and its original surface figure accuracy after ion beam figuring. (Image by XIOPM)


