Eye tracking is a powerful method to investigate the relationship between behavior and neural mechanisms. In recent years, eye movement analysis has been used in patients with neurological disorders to assess cognitive function. In this review, we explore the latest eye tracking researches in neurological disorders that are commonly associated with cognitive deficits, specifically, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), Alzheimer’s disease (AD), Parkinson’s disease (PD), multiple sclerosis (MS), and epilepsy. We focus on the application of ocular measures in these disorders, with the goal of understanding how eye tracking technology can be used in the clinical setting.
Eye tracking tasks (especially saccadic tasks) are often used as an adjunct to traditional scales for cognitive assessment. Eye tracking data confirmed that executive dysfunction is common in PD and ALS, whereas AD and MS are characterized by attention deficits. Research in evaluating cognitive function in epilepsy using eye tracking is still in its early stages, but this approach has shown advantages as a sensitive quantitative method with high temporal and spatial resolution.
Eye tracking technology can facilitate the assessment of cognitive impairment with higher temporal resolution and finer granularity than traditional cognitive assessment. Oculomotor data collected during cognitive tasks can provide insight into biological processes. Eye tracking provides a nonverbal and less cognitively demanding method of measuring disease progression in cognitively impaired patients.
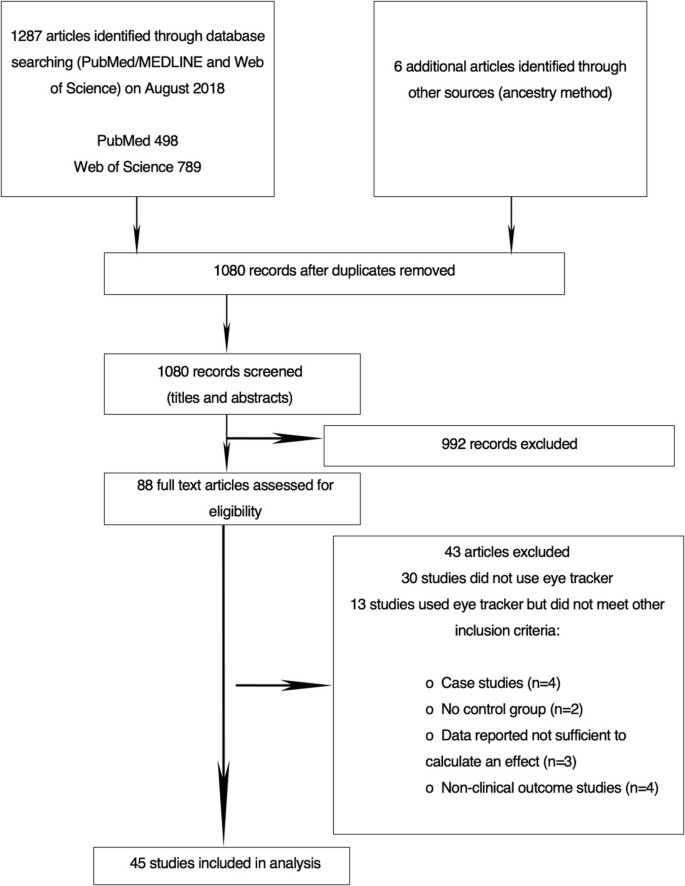
Systematic review search process. (Image by XIOPM)


