A research team led by Dr. SUN Qibing from Xi'an Institute of Optics and Precision Mechanics (XIOPM) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) investigates the influence of third-order dispersion of dispersive elements, three-photon absorption and free-carrier effects on mid-infrared time magnification via four-wave mixing (FWM) in Si0.8Ge0.2 waveguides.
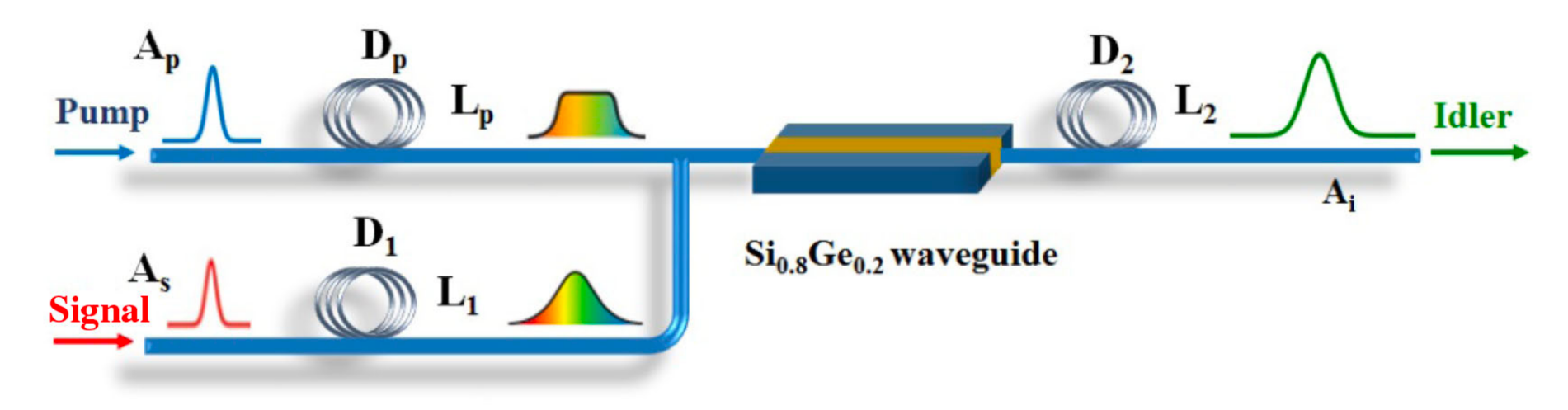
Operation principle of the time magnification based on FWM in the Si0.8Ge0.2 waveguide. (Image by XIOPM)
It is found that the magnified waveform is seriously distorted by these factors, and conversion efficiency is decreased, mainly because of nonlinear absorption.
A time lens based on FWM in Si0.8Ge0.2 waveguides is proposed for time magnification of mid-infrared ultrashort pulses, in which the low-distortion, high-magnification in the time domain could be obtained by optimizing system parameters.
These results make it possible to analyze the transient dynamic process through oscilloscopes and detectors with gigahertz bandwidth and have important applications in ultrafast process analysis, optical pulse sampling, and optical communications.
(Original research article “Applied Optics” (2020) https://doi.org/10.1364/AO.379232)


