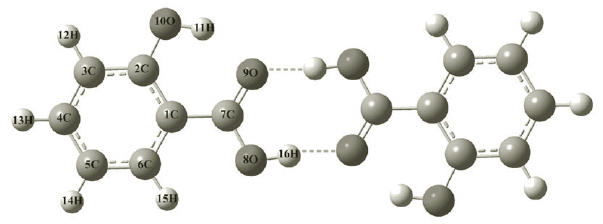
A research team measure the terahertz spectra of salicylic acid and sodium salicylate by broadband terahertz time-domain spectroscopy (THz-TDS). Two absorption features of salicylic acid and three characteristic features of sodium salicylate are reported for the first time. Their investigation shows that salicylic acid and sodium salicylate can be easily distinguished based on their distinctive THz spectra, which could be attributed to their intra- and intermolecular structure differences. Furthermore, solid-state density functional theory calculations reveal that the absorption features of salicylic acid mainly originate from intermolecular interactions, except for the absorption feature at 2.28 THz, while gaseous-state theory calculations show that the absorption features of sodium salicylate mainly come from intramolecular vibrations except for the absorption feature at 0.40 THz. Our investigation indicates that THz vibrational modes are highly sensitive to molecular structures and intermolecular interactions, promoting the application of THz spectroscopy in distinguishing chemicals and pharmaceuticals with similar molecular structures.
(Original research article "Journal of Applied Spectroscopy Vol. 85, Issue 6, pp. 1143-1150 (2019) https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs10812-019-00773-w")


